Spoofing is the most sophisticated form of interference and is difficult to be detected. It is a malicious attack that can manipulate various parameters, such as timing information, ranging information, and ephemeris data, leading the receiver to provide false information.
A spoofing attack can be categorized as either time-unsynchronized or time-synchronized, depending on the synchronization of the spoofer with GNSS satellites.
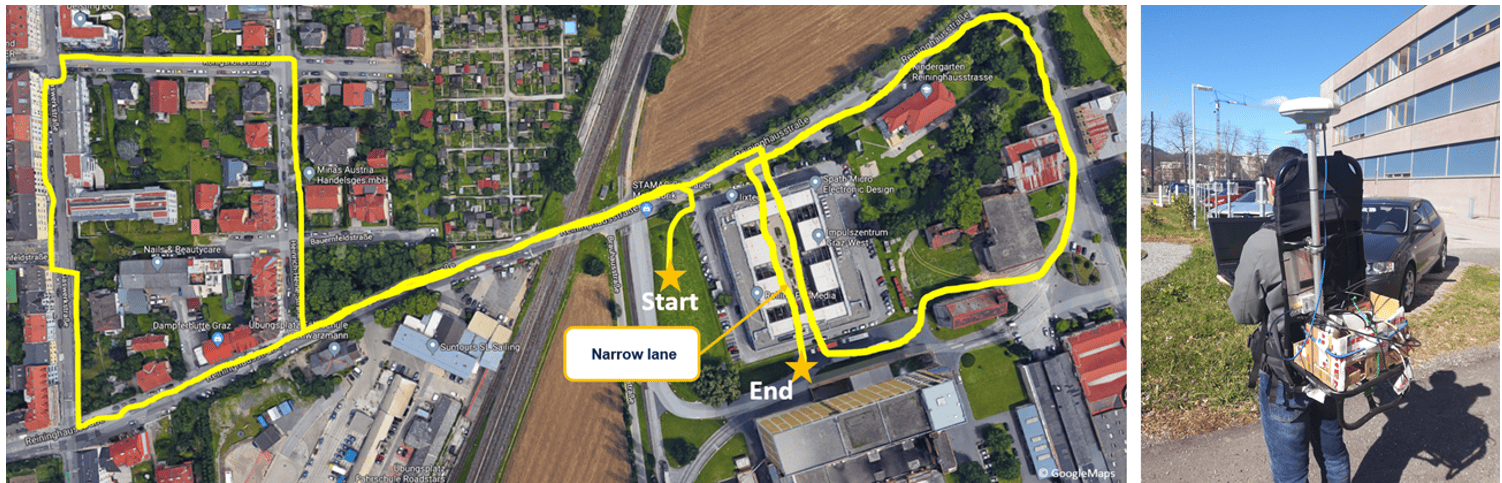
This product is a sample package on L1/E1 frequency recorded by an SX3 front-end mounted on a driving car. In this scenario, a time-synchronized position spoofing is generated over the air by a LOKI device to change the position.
Both LOKI generator and the target receiver were configured to work with GPS L1 and Galileo E1 signals. The car followed a predetermined street at a speed of 50 km/h. LOKI was used to initiate the spoofing of the car as soon as it entered the spoofed red area. The receiver was continuously spoofed by a transmitting antenna that always targeted the moving car. Even when the car was still moving on the street (green line), the attacked GNSS receiver displayed the spoofed trajectory (red line).
Details:
- Record Condition: Open sky, dynamic (driving car)
- Length: ≈ 3 Minutes
- Sampling Frequency: 20 MHz
- Bit Resolution: 2 Bits
- Scenario: Time-synchronized position spoofing (generated by a LOKI device over the air*)
* IGASPIN had exclusive permission for this test to transmit the GNSS spoofing signal over the air.