Spoofing is the most sophisticated form of interference and is difficult to be detected. It is a malicious attack that can manipulate various parameters, such as timing information, ranging information, and ephemeris data, leading the receiver to provide false information.
A spoofing attack can be categorized as either time-unsynchronized or time-synchronized, depending on the synchronization of the spoofer with GNSS satellites.
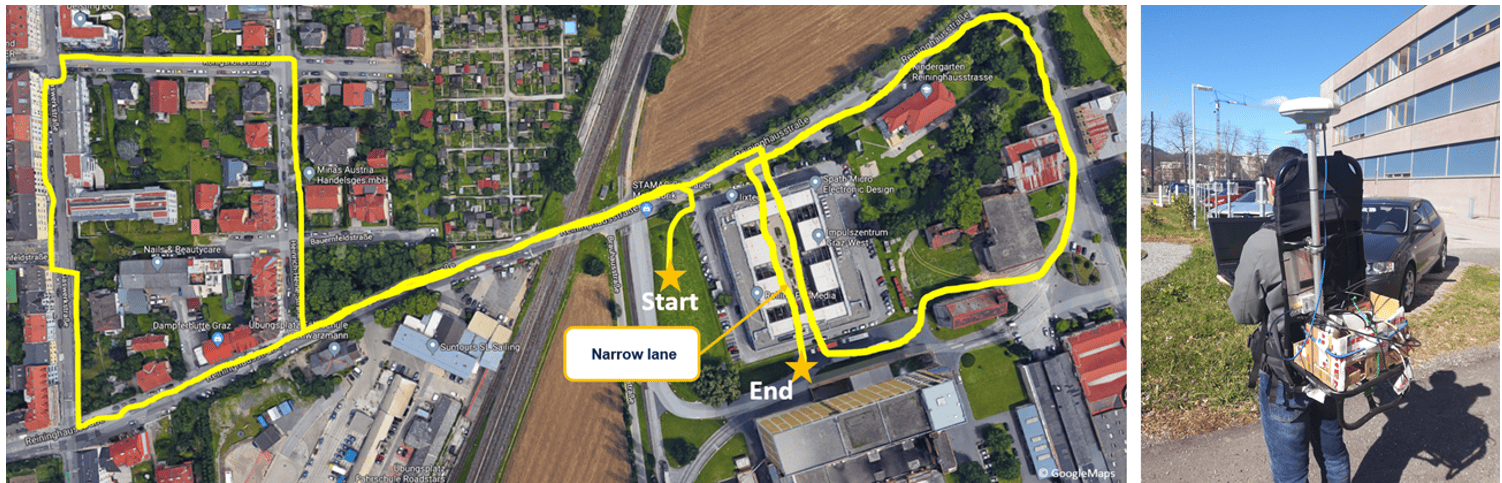
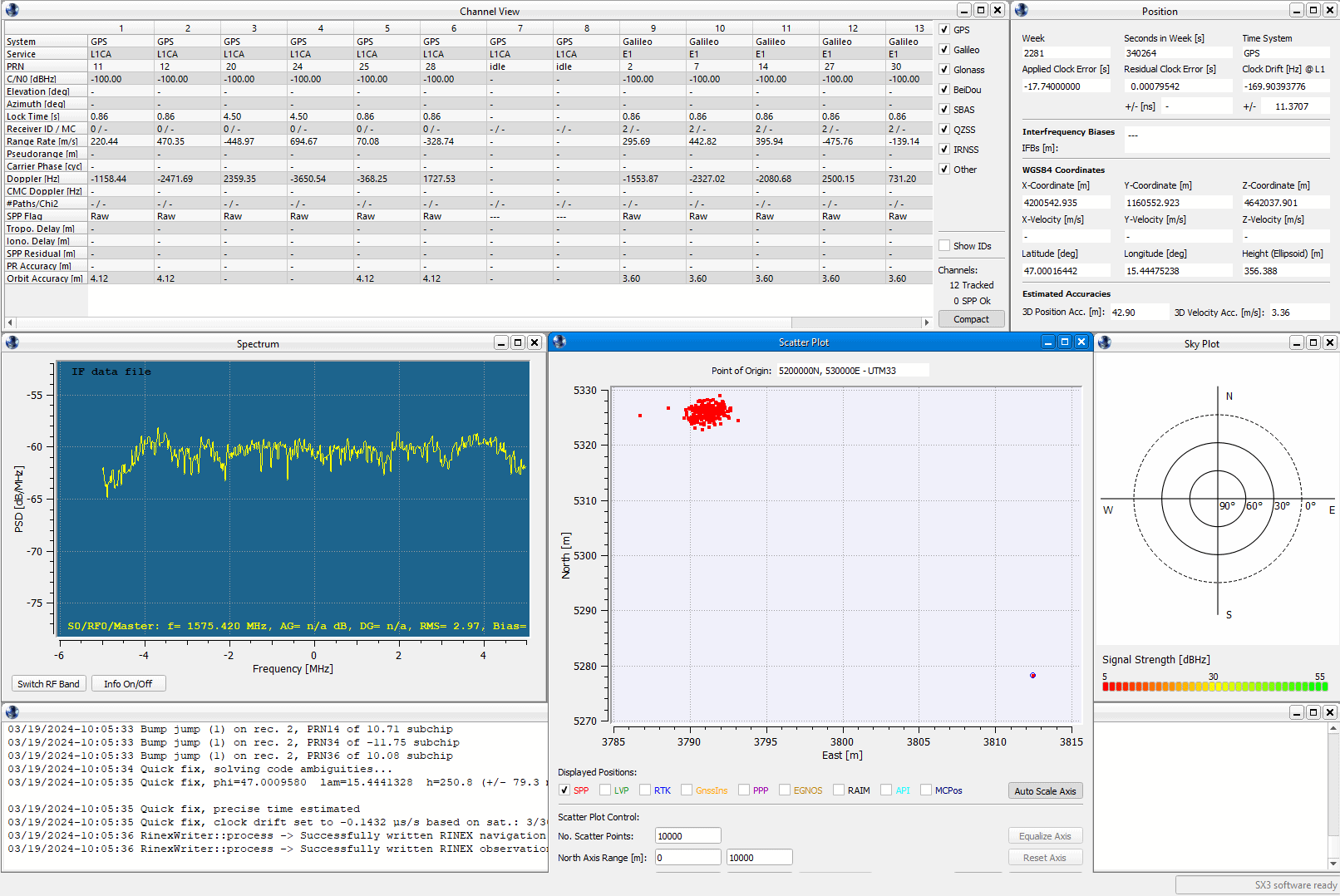
This product is a sample package on L1/E1 frequency recorded by an SX3 front-end in an open-sky environment. In this scenario, a time-synchronized position spoofing over the air is generated by a LOKI device.
Details:
- Record Condition: Open sky, static
- Length: ≈ 4 Minutes
- Sampling Frequency: 20 MHz
- Bit Resolution: 2 Bits
- Scenario: Time-synchronized position spoofing (generated by a LOKI device over the air*)
* IGASPIN had exclusive permission for this test to transmit the GNSS spoofing signal over the air.